Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function
Authors
08-23-2017
12:00pm
PST
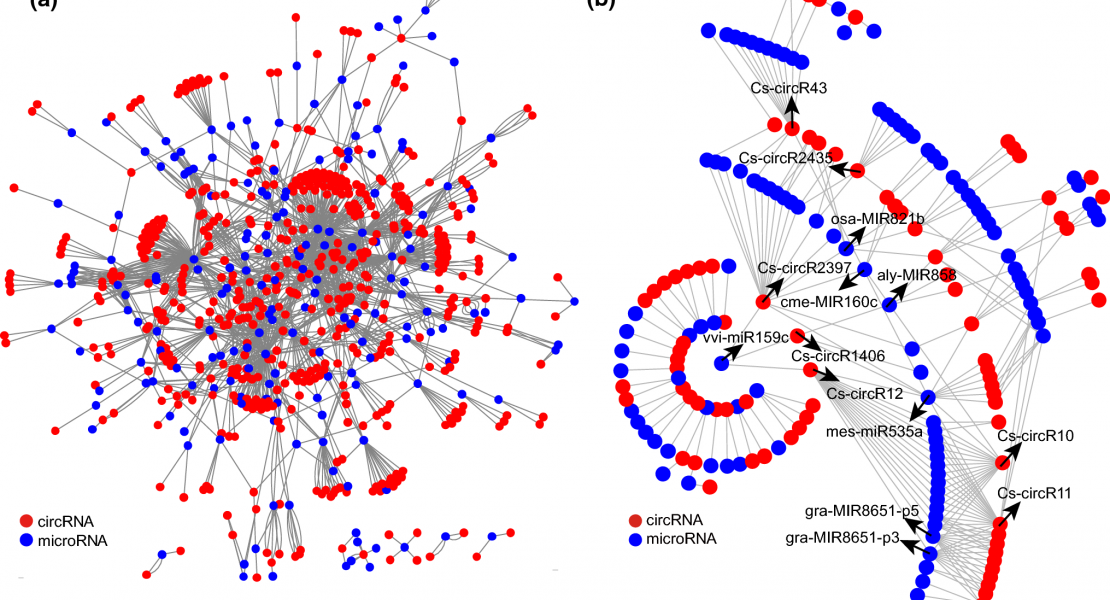
Abstract
Hundreds of circular RNAs (circRNAs) are highly abundant in mammalian brain, with oftentimes conserved expression. Here, we show that the circRNA Cdr1as is massively bound by miR-7 and miR-671 in the human and mouse brain. When the Cdr1as locus was removed from the mouse genome, knockout animals displayed impaired sensorimotor gating, a deficit in the ability to filter out unnecessary information associated with neuropsychiatric disorders. Electrophysiological recordings revealed dysfunctional synaptic transmission. Expression of microRNAs miR-7 and miR-671 was specifically and post-transcriptionally misregulated in all brain regions analyzed. Expression of immediate early genes such as Fos, a direct miR-7 target, was enhanced in Cdr1as-deficient brains, providing a possible molecular link to the behavioral phenotype. Our data indicate an in vivo loss-of-function circRNA phenotype and suggest that interactions between circRNAs and miRNAs are important for normal brain function.
